1971
Approval of loan
for shipyard construction
A&P Appledore Chairman Charles Longbottom
was persuaded with a KRW 500 banknote featuring the turtle ship,
leading to Barclays Bank’s approval of the loan
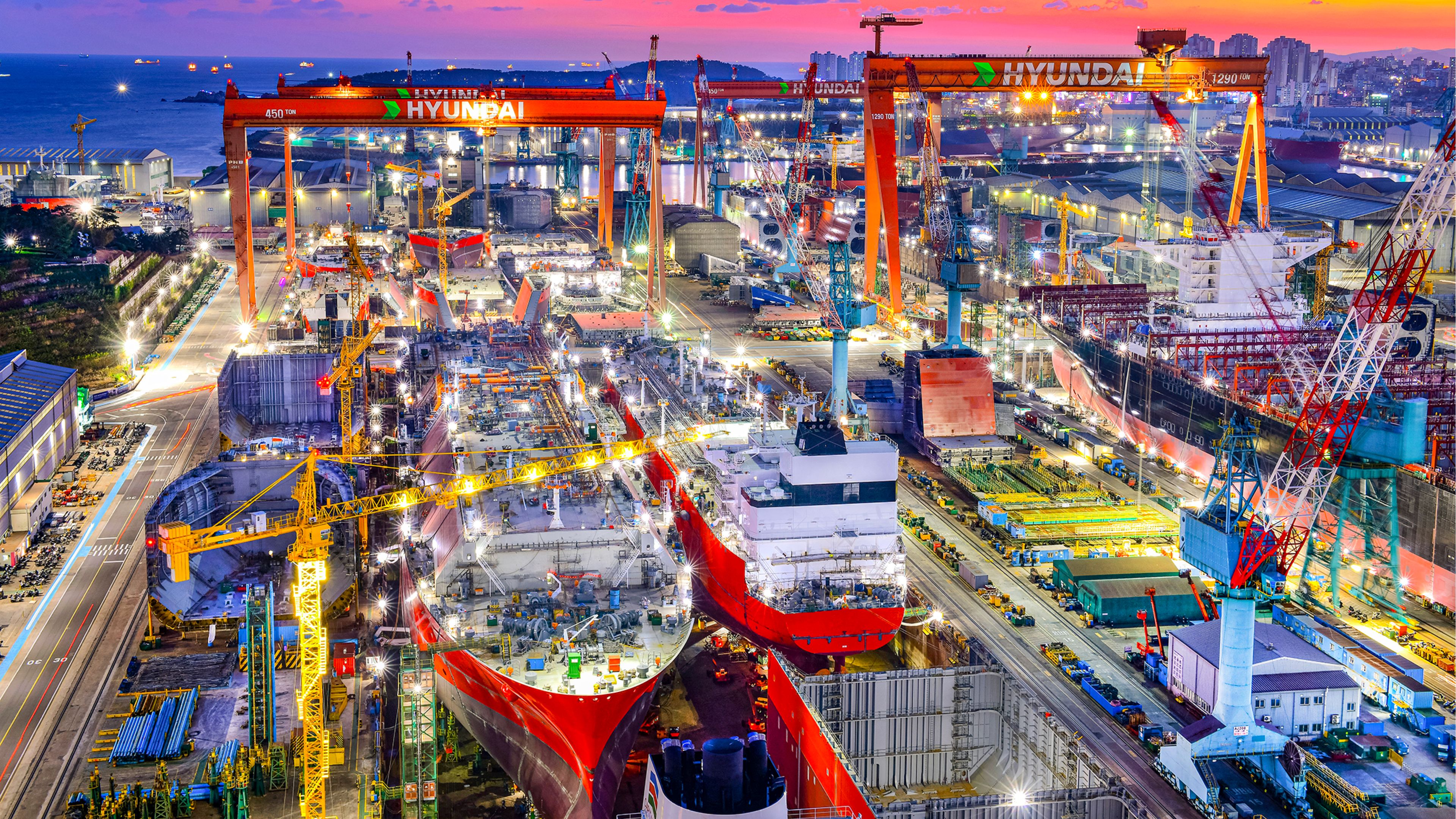










1971
Approval of loan for shipyard construction
A&P Appledore Chairman Charles Longbottom was persuaded with a KRW 500 banknote featuring the turtle ship, leading to Barclays Bank’s approval of the loan
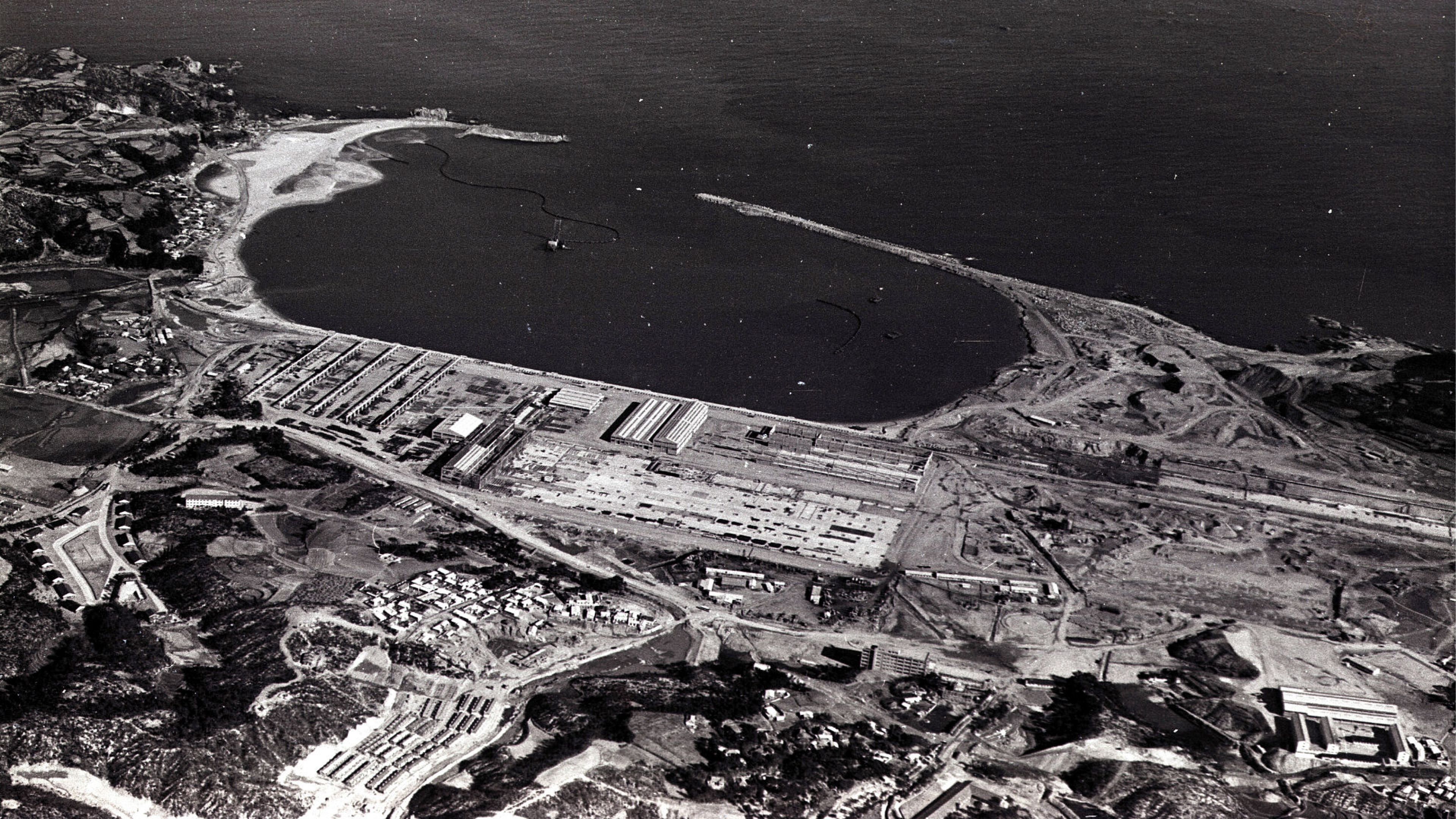
1972
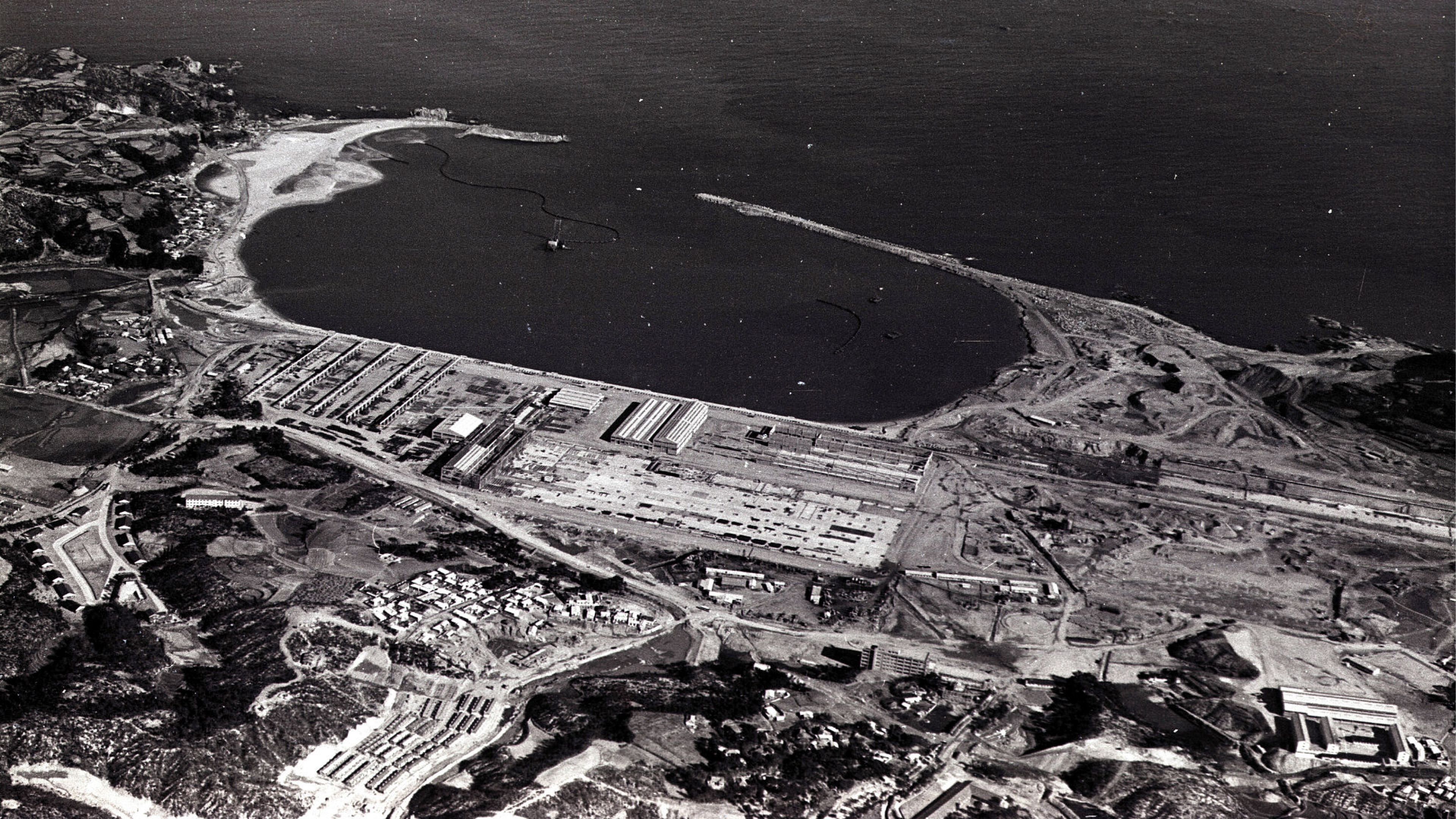
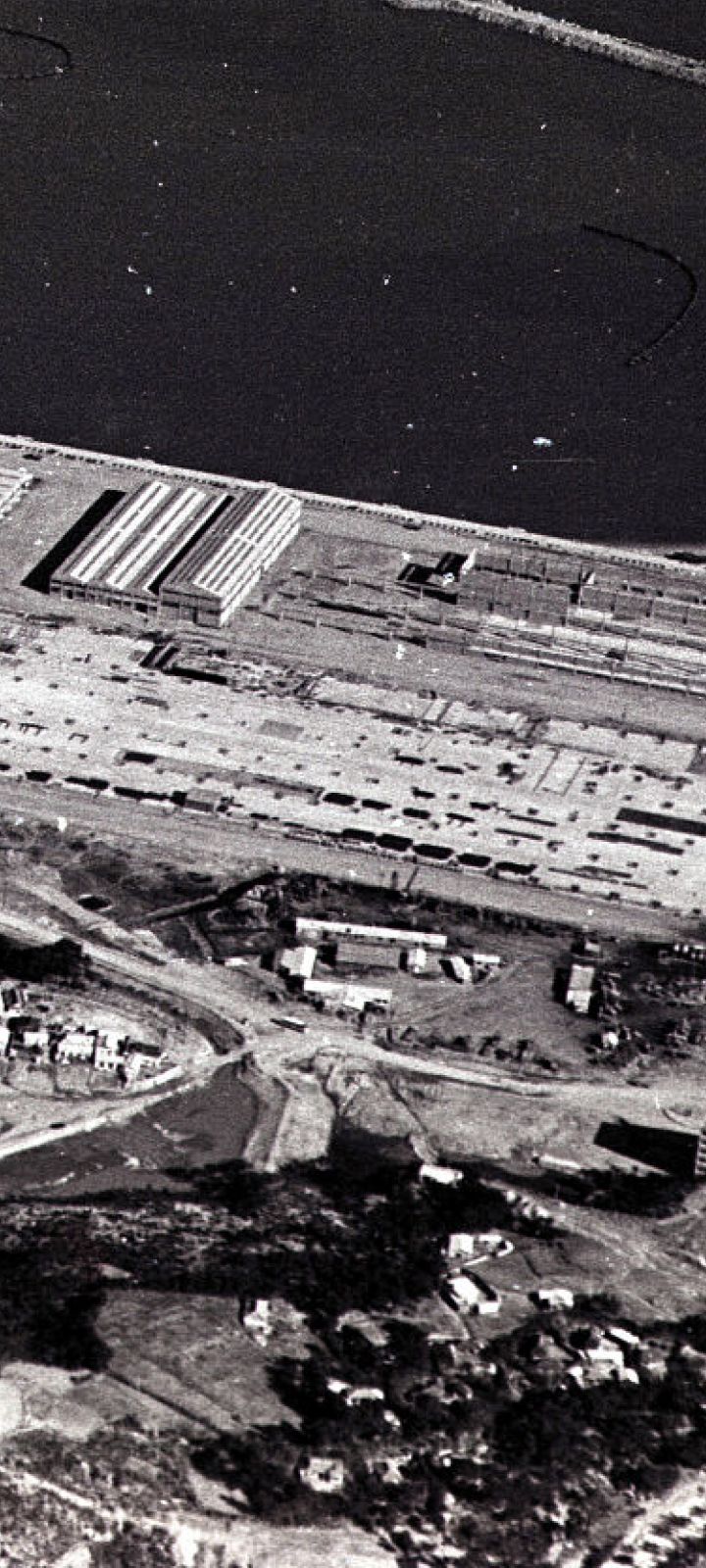
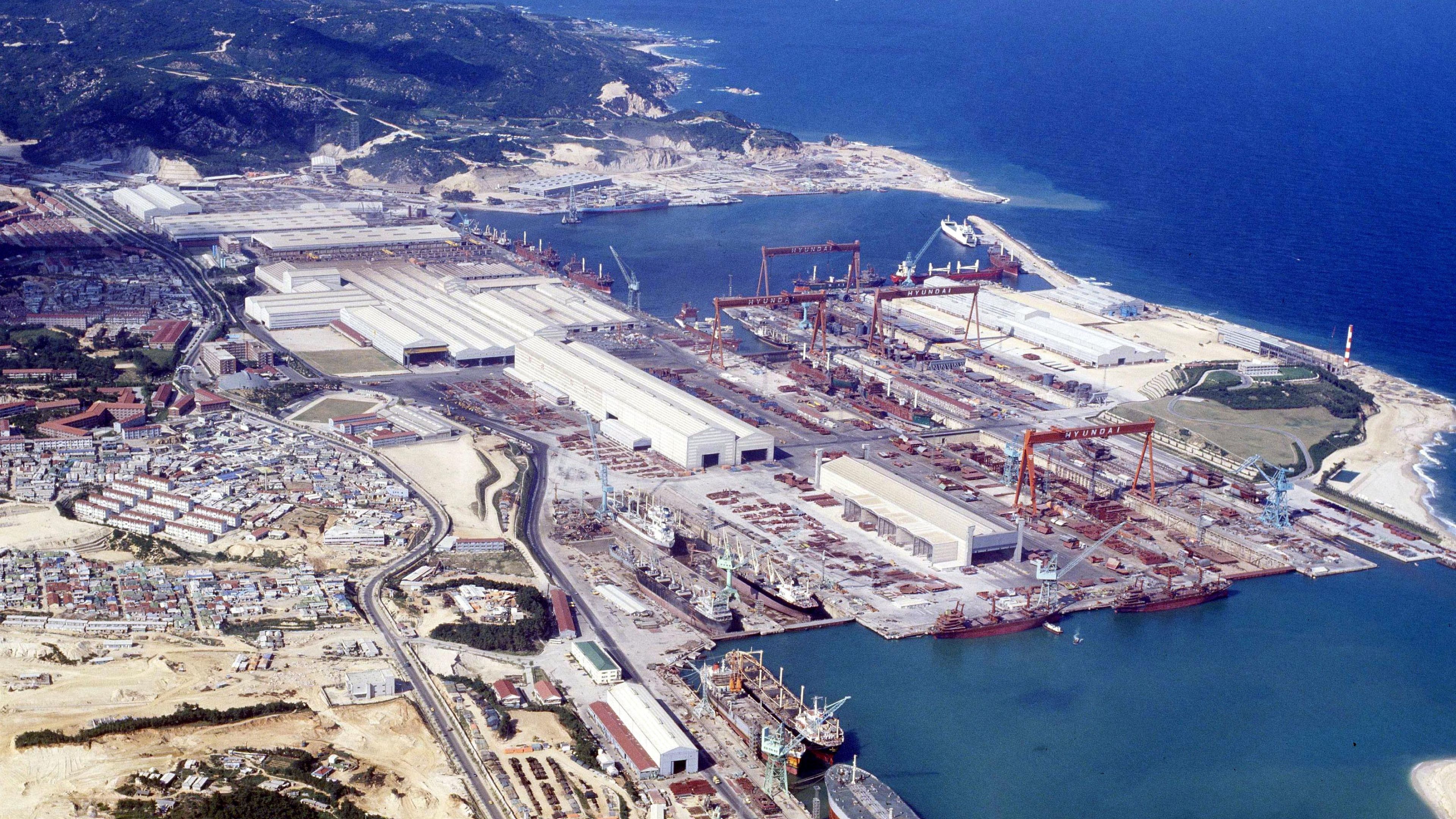
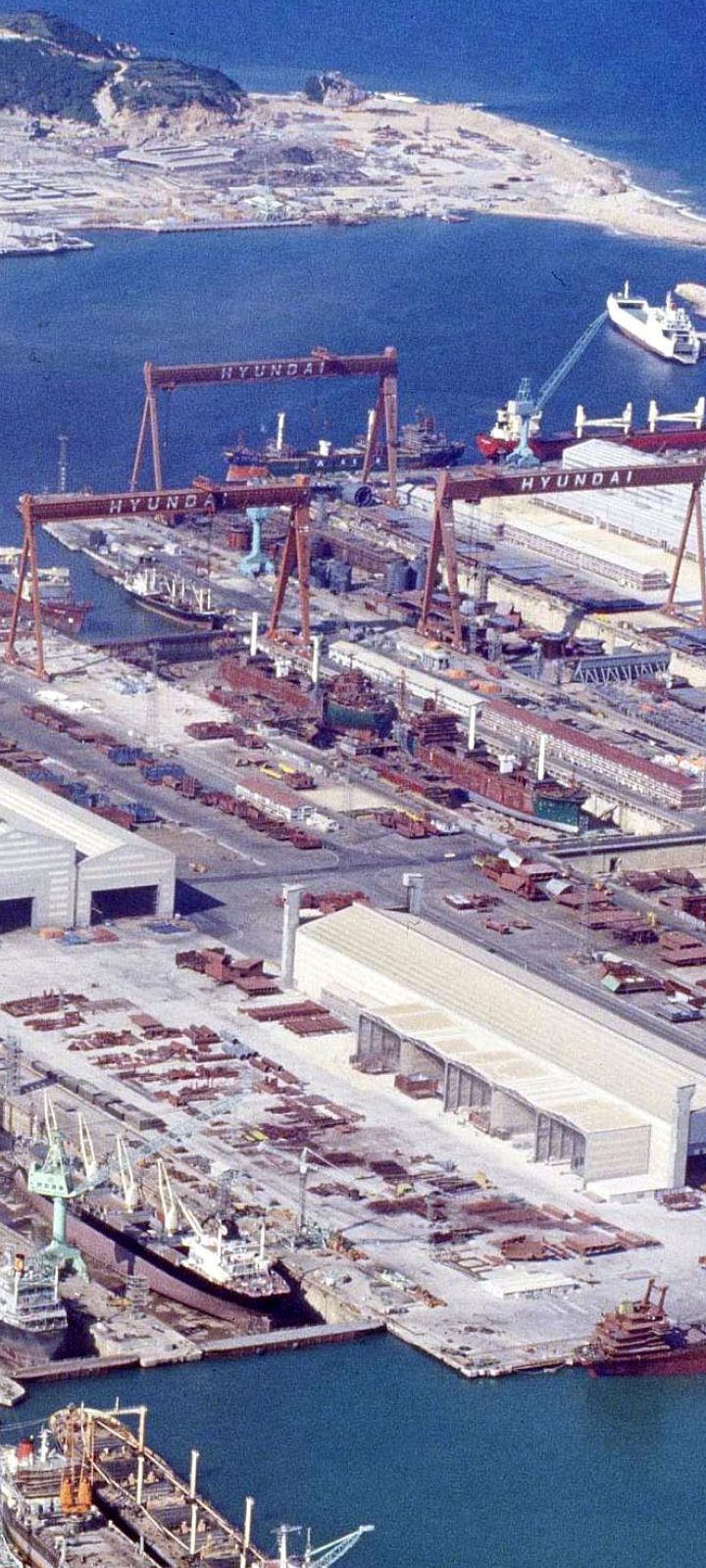
Groundbreaking ceremony for the Ulsan Shipyard
A groundbreaking ceremony for the Ulsan Shipyard was held in March 1972 The groundbreaking was attended by then-President Park Chung-hee, government ministers, and ambassadors from various countries, marking the birth of Korea’s shipbuilding industry
1974
Simultaneous completion of the shipyard and two supertankers
In just two years and three months after the groundbreaking in March 1972, the company completed the shipyard and successfully built two supertankers—setting a historic milestone in global shipbuilding
1979
Production of the first marine engine
In May 1979, Hyundai Heavy Industries produced its first domestically built marine engine, the 9,380-horsepower Hyundai B&W 7L55GF, which was installed in the 25,000-ton bulk carrier “Haejeong (海貞)” ordered by Shinhan Shipping
1980
Held a naming ceremony for ROKS Ulsan, Korea’s first warship
In December 1980, a handover and naming ceremony was held for Korea’s first warship, ROKS Ulsan. With the successful construction of the 2,000-ton ROKS Ulsan, HD Hyundai Heavy Industries positioned Korea as a warship-producing nation
1983
Selected as the world's number one shipyard
In 1983, HD Hyundai Heavy Industries was named the world’s number one shipyard That year, the company built 2.226 million tons of ships, achieving the world’s highest shipbuilding volume
1994
Construction of Korea’s first LNG carrier
The vessel, named “Hyundai Utopia,” was Korea’s first LNG carrier and could transport natural gas in a 125,000 ㎥ tank The localization of LNG carrier production, a representative high value-added vessel, positioned Korea as a leader in advanced shipbuilding
2000
Development of “HiMSEN,” a proprietary medium-duty engine
In August 2000, after about 10 years of development, the company completed proprietary development of the medium-duty HiMSEN engine, reinforcing its status as a global engine maker—despite early skepticism
2001
Completion of the world’s largest deep sea FPSO
In February 2001, a completion ceremony was held for the Girassol FPSO, the company’s first newbuild FPSO. Successfully completing the world’s largest FPSO project at the time, the company emerged as a major player in offshore equipment
2002
Launch of Hyundai Heavy Industries Group (now HD Hyundai Group)
In February 2002, the spin-off of Hyundai Heavy Industries was approved. Upon its launch, Hyundai Heavy Industries Group announced its commitment to enhancing corporate value through transparent and rational management
2007
Launch of ROKS Sejong the Great, Korea’s first Aegis destroyer
In May 2007, HD Hyundai Heavy Industries held a launching ceremony for ROKS Sejong the Great (KDX-III), Korea’s first 7,000-ton Aegis destroyer. Construction of the Aegis destroyer marked Korea’s first and the world’s third successful Aegis warship program.
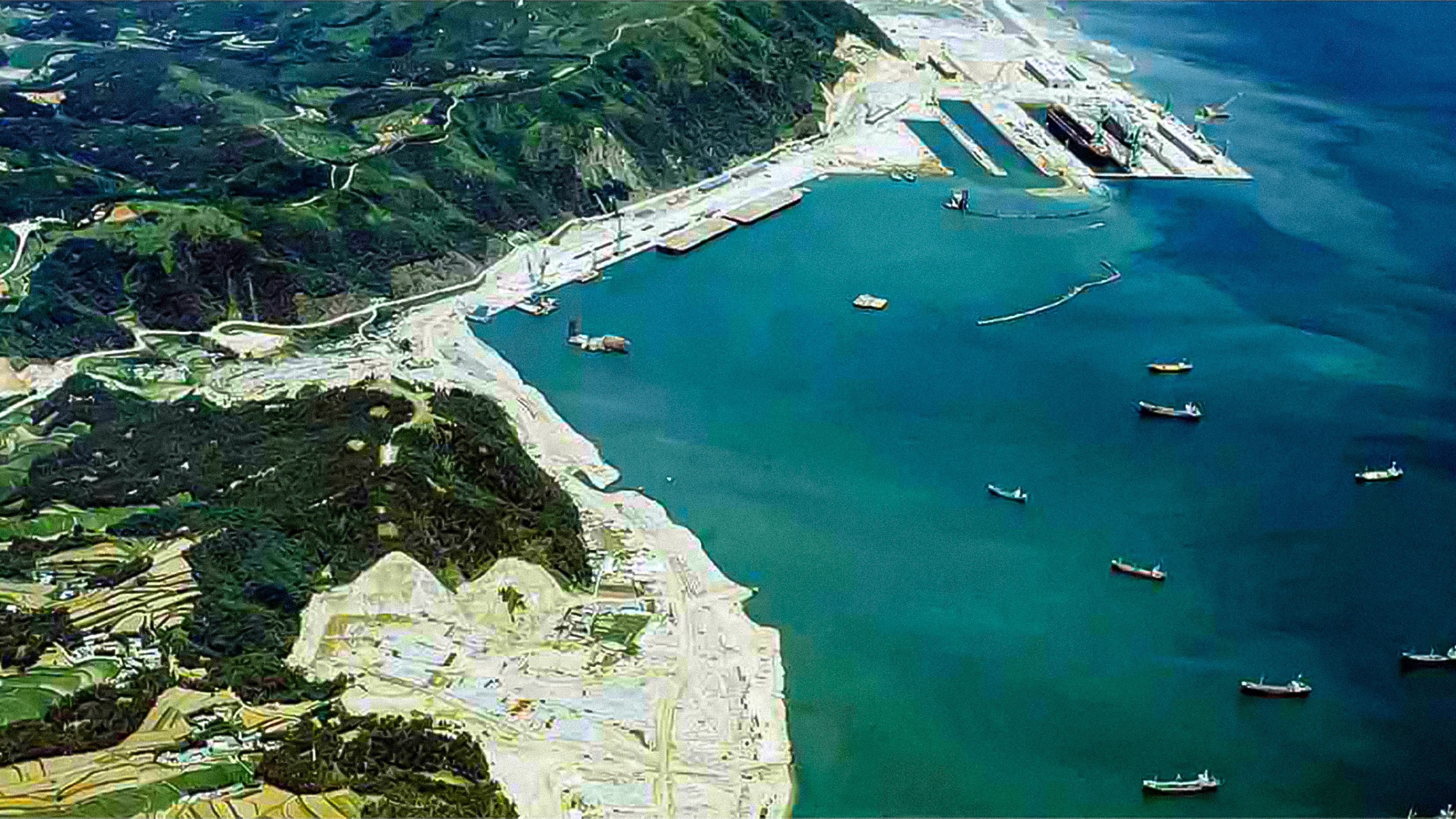
2009
Completion of the Marine H Dock
HD Hyundai Heavy Industries completed the world’s first FPSO dock, setting a global precedent in offshore construction. KRW 140 billion was invested in the H Dock, Hyundai Heavy Industries’ tenth dock, which has a capacity of 1 million tons—the largest in the world
2012
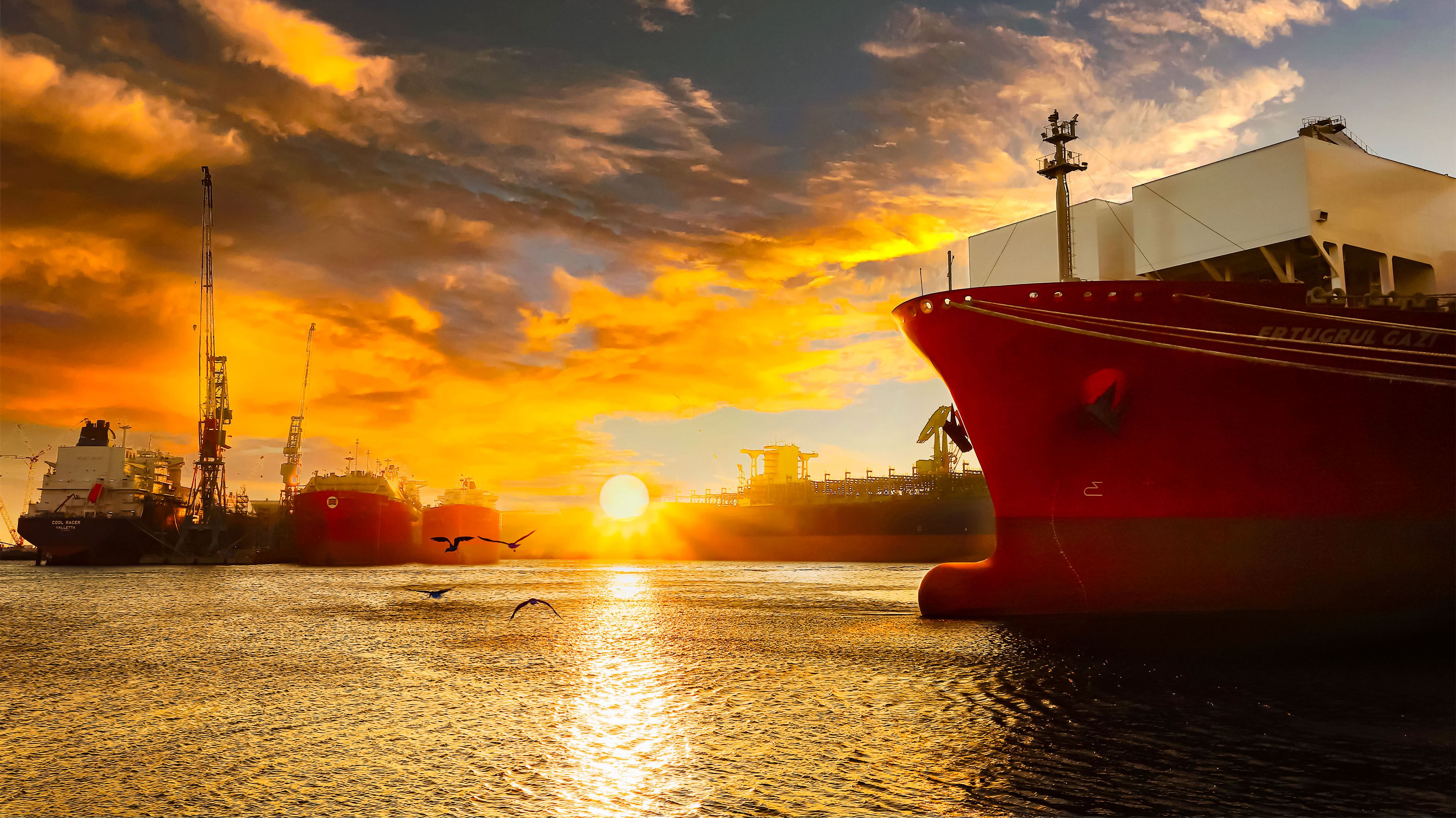
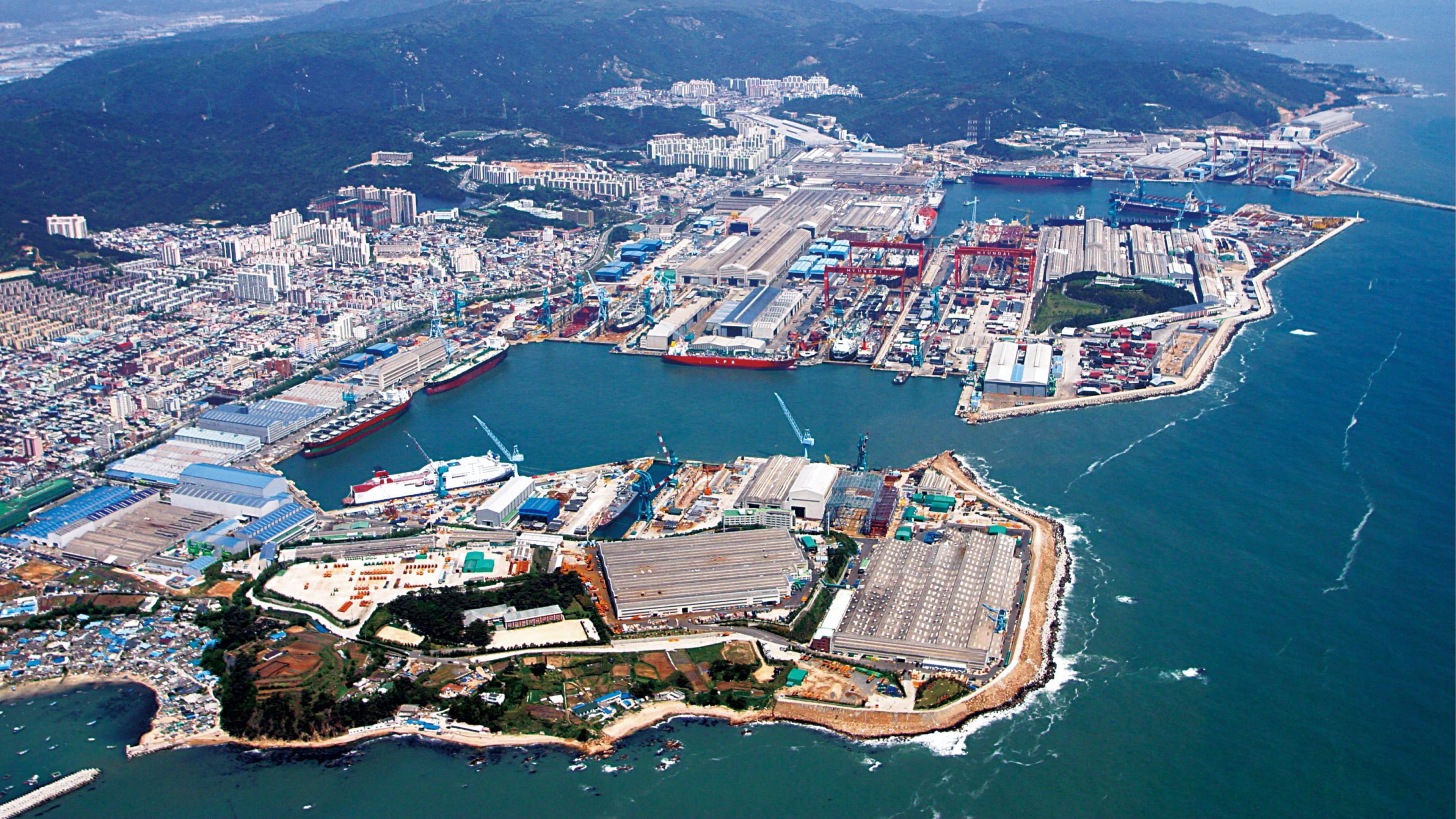
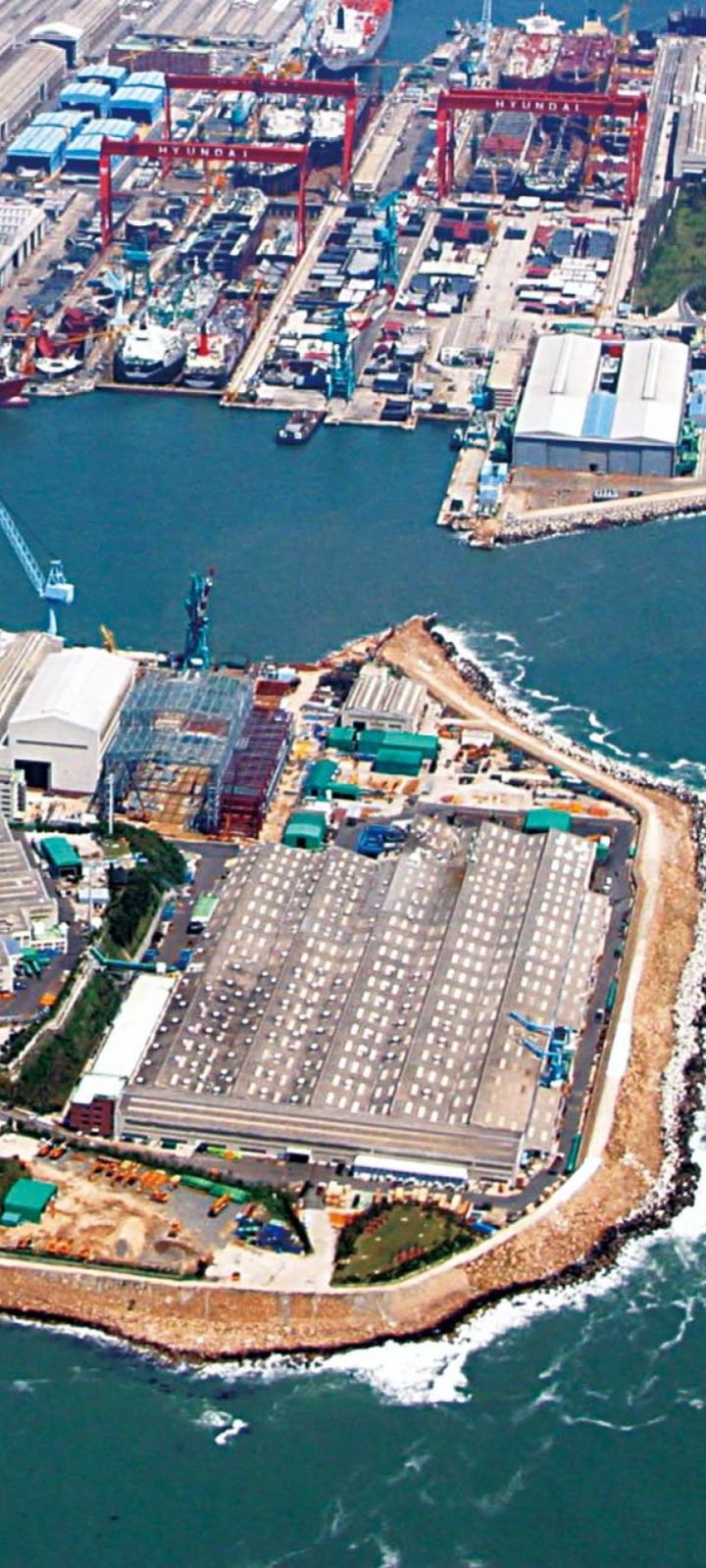
Surpassing the 100 million GT milestone
In March 2012, 40 years after the first groundbreaking, the company reached 107.17 million GT in shipbuilding volume. By continuously developing new construction methods—such as onshore building, ship submersion (沈水), and T-docks—the company expanded its shipbuilding capacity and significantly shortened construction periods. As a result, it became the world’s first shipbuilder to surpass 100 million GT
2014
Delivery of the world's first floating LNG storage regasification unit (FSRU)
FSRUs are more efficient than conventional onshore LNG terminals, with lower construction costs and shorter installation times This technology has enabled HD Hyundai Heavy Industries to secure a leading position in the global LNG market and continue advancing eco-friendly ship and equipment development
2020
Production of Korea’s first LPG dual fuel engine
LPG dual-fuel propulsion technology enables the use of both diesel and liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). HD Hyundai Heavy Industries leads in eco-friendly shipbuilding and supports the global shipping industry’s carbon neutrality goals
2023
Change of company name to HD Hyundai Heavy Industries
In 1978, the company changed its name from Hyundai Shipbuilding Heavy Industries to Hyundai Heavy Industries. After 45 years, the name was changed again to HD Hyundai Heavy Industries to begin a new chapter in the company’s future
2025
Merged HD Hyundai Mipo into HD Hyundai Heavy Industries
2025
Last Year
마지막 년도는 내용이 노출되지 않습니다.


2026
A new history made
by
HD Hyundai
Heavy Industries
The past 50 years for
HD Hyundai Heavy Industries
have been a glorious history
of challenges and growth,
writing a chapter
in our nation's economic
development.
The next 50 years that begins this year
will be a history of innovation
and creation
which merges technology,
environment, and digital
advancements.